Foreign Direct Investment refers to investment made by a foreign individual or company into business ventures in another country, often through establishing operations, acquiring assets, or purchasing shares in local businesses. For Pakistan, Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan is a vital driver of economic growth, offering numerous benefits such as job creation, technology transfer, and a boost to local industries. It helps improve infrastructure, enhances productivity, and strengthens the overall economy.
In this blog, we will explore the current trends in Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan, identify key sectors attracting foreign investments, and highlight the opportunities available for investors. Whether you’re a potential investor or simply interested in Pakistan’s economic landscape, this guide will provide valuable insights into why Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan matters now more than ever.
What Is Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan & Why It Matters
Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan is when a person or company from one country invests directly in a business or asset in another country. This type of investment usually involves setting up operations, like building factories, purchasing a company, or expanding an existing business.
Unlike other forms of foreign investment, such as portfolio investments (where investors buy stocks or bonds in foreign markets without gaining control of a business), Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan involves a long-term commitment and a more active role in the local economy.
Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan is crucial for Pakistan’s growth, as it brings several key benefits:
- Job Creation: When foreign companies invest in Pakistan, they often build factories or set up offices, creating new jobs for the local workforce. For example, when a global tech company opens a factory, it employs local workers, boosting employment.
- Technology and Expertise Transfer: Foreign investors often bring in advanced technology and management techniques, helping local businesses improve their processes. This can raise the overall efficiency of industries in Pakistan, like the textile or manufacturing sectors.
- Export Growth: Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan can lead to more local businesses producing goods for export. For instance, if a foreign company invests in Pakistan’s agricultural sector, it might help improve farming techniques, leading to better-quality produce for international markets.
- Infrastructure Development: Foreign investments often contribute to improving a country’s infrastructure. For example, the construction of new roads, ports, and energy plants may be a part of foreign investment deals, which helps boost the economy in the long run.
The Current State of Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan (2025)
Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan has shown mixed trends, with occasional growth despite economic challenges. Here’s a breakdown of the current situation:
Recent Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan Trends
- November 2025: Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan increased by $179 million compared to prior months.
- FY 2024–25 (H1): Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan inflows reached USD 1.33 billion, reflecting a growth trend.
Long-Term Investment Levels
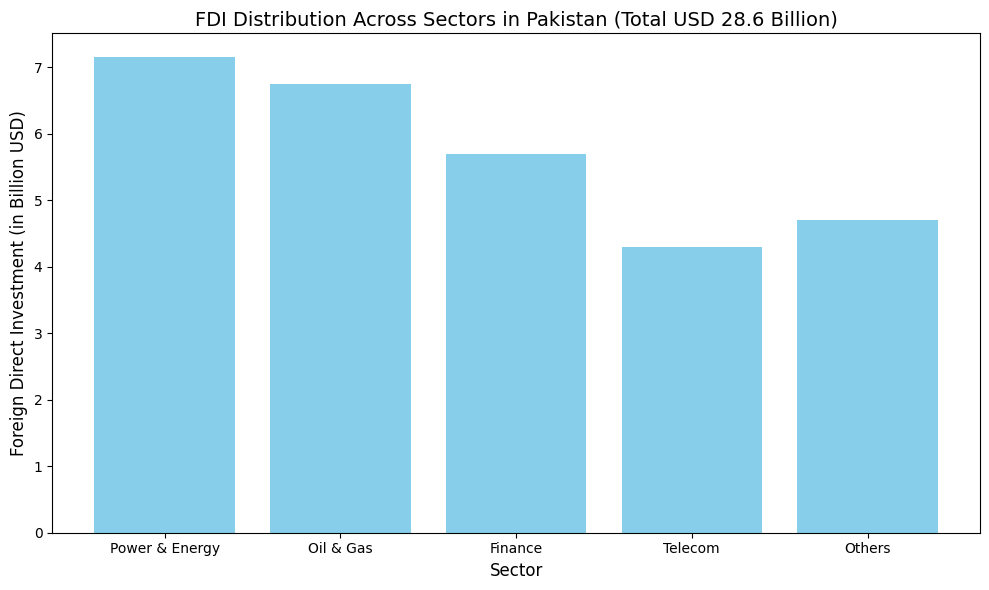
- Cumulative Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan stock: Approximately USD 28.6 billion by the end of 2022.
- Key sectors: Power, oil & gas, finance, telecom are the primary recipients of foreign investment.
Volatility in Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan Inflows
- Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan is volatile due to factors like political instability, inflation, and exchange rate fluctuations.
- Some months see lower inflows, especially during periods of political uncertainty.
Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan as a Percentage of GDP
- Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan contributes around 1-2% of Pakistan’s GDP, supplementing domestic investments and supporting key sectors.
- Historical data shows fluctuations, but overall foreign direct investment in Pakistan remains an important part of the economy.
Key Sources of Foreign Investment in Pakistan

Foreign direct investment in Pakistan comes from several key countries, each contributing significantly to various sectors of the economy. Here’s a breakdown of the major investors:
1. China: The Largest Investor
- Share of FDI: Over 25% of total foreign investments
- Key Projects:
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC): A major infrastructure initiative involving roadways, energy projects, and industrial zones.
- Sectors: Energy, infrastructure, transport, industrial zones
- Impact: Long-term investment focusing on connectivity and economic development.
China’s investments are largely concentrated in energy and infrastructure, with the CPEC project acting as the backbone of its economic partnership with Pakistan.
2. United Kingdom
- Investment Focus:
- Financial services
- Telecommunications
- Consumer goods
- Energy
- Contribution: Strong trade ties and joint ventures in various sectors
- Key Advantage: Long-standing historical connections that foster trust and collaboration between both countries.
3. Hong Kong
- Investment Focus:
- Banking
- Manufacturing
- Technology
- Contribution: Facilitates investments from mainland China and other global investors.
- Key Advantage: Favourable tax policies and business environment for companies seeking to operate in Pakistan.
4. United States and Switzerland
- United States:
- Investment Focus: Technology, consumer goods, financial services
- Key Contribution: US companies are involved in setting up joint ventures and technology-based investments.
- Switzerland:
- Investment Focus: Energy, industrial sectors, and pharmaceuticals
- Key Contribution: Swiss investors are significant in managing resources, energy projects, and pharmaceutical investments.
Foreign Investment Breakdown by Country
| Country | Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan Share | Primary Sectors | Key Projects |
| China | 25%+ | Energy, Infrastructure, Transport | CPEC (Energy, Roads, Industrial Zones) |
| United Kingdom | Moderate | Financial Services, Telecommunications, Energy | Joint Ventures, Infrastructure Projects |
| Hong Kong | Moderate | Banking, Manufacturing, Technology | Investment Facilitation from China |
| United States | Moderate | Technology, Consumer Goods, Finance | Technology, Joint Ventures |
| Switzerland | Moderate | Energy, Pharmaceuticals, Industrial | Energy Projects, Industrial Ventures |
Top Sectors Attracting Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan

Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan is flowing into several key sectors that show strong growth potential and opportunities. These sectors not only contribute to the country’s economic development but also present promising returns for foreign investors. Here are the major sectors that are attracting the most foreign investment:
- Power & Energy
- Why it’s appealing: Pakistan’s power sector faces huge capital demands due to energy shortages and the need for modern infrastructure. The government’s efforts to privatise state-owned companies and offer incentives for foreign investors in renewable energy and traditional power generation make it an attractive sector.
- Key opportunity: Investment in solar, wind energy, and hydropower projects is growing, as the country shifts toward more sustainable and cost-effective sources of energy.
- Oil & Gas
- Why it’s appealing: Pakistan is home to significant oil and gas reserves, particularly in its northern and southwestern regions. As energy consumption increases, there’s a need for modernising and expanding extraction and refining capacities.
- Key opportunity: Foreign investors are particularly interested in the exploration, production, and distribution of oil and gas, with companies aiming to meet the growing domestic demand and export potential.
- Financial Services (Banks & Insurance)
- Why it’s appealing: The financial services sector is rapidly expanding as Pakistan’s middle class grows, leading to more demand for banking, insurance, and investment services. The government is pushing for financial inclusion and improving the regulatory environment, which encourages foreign investment.
- Key opportunity: There’s an increasing demand for digital banking, insurance, and fintech solutions, with foreign investors looking to partner with or acquire local banks and financial institutions.
- IT & Telecom
- Why it’s appealing: Pakistan’s digital economy is booming, and the country has a growing tech-savvy youth population. The IT sector, including software development and tech startups, offers tremendous potential for growth. The telecom sector is also expanding, with increasing mobile and internet penetration.
- Key opportunity: Investors are particularly focused on the IT outsourcing, mobile networks, and digital infrastructure, which are essential for the country’s evolving digital landscape.
- Infrastructure & Transport
- Why it’s appealing: Pakistan’s strategic location as a gateway to Central Asia and the Middle East makes infrastructure development crucial for trade and commerce. Investments in roads, ports, and airports are growing, especially as the country is working to develop its CPEC (China-Pakistan Economic Corridor) projects.
- Key opportunity: Logistics, road networks, ports, and railway projects are major areas where foreign investors see high returns, particularly in public-private partnerships.
- Real Estate & Construction
- Why it’s appealing: With a rapidly growing urban population and increasing demand for housing, Pakistan’s real estate and construction sectors are experiencing a boom. There’s significant potential in both residential and commercial property development.
- Key opportunity: Residential developments, retail spaces, and mixed-use developments are attracting foreign investors, especially in major cities such as Karachi, Lahore, and Islamabad, where demand for real estate continues to rise.
Investment Opportunities in Pakistan

| Opportunity Area | Key Details | Growth Potential |
| Special Economic Zones & Policy Supports | Islamabad Model SEZ, $2.5B investment target, incentives for investors | High, Tax breaks, improved regulations, fast approvals |
| Technology & Digital Economy | IT outsourcing, fintech innovations, and growing demand for digital solutions | High, expanding tech industry and digital services |
| Green Energy & Solar Power | Solar power, renewable energy initiatives | High, Vast solar potential, government incentives |
| Manufacturing & Exports | Garments, electronics, and industrial production | Moderate, Increased demand, labour cost advantages |
| Agriculture & Food Processing | Large domestic market, modernising agricultural practices | Moderate, Export potential and local consumption growth |
| Real Estate & Urban Growth | Urbanisation is driving housing and commercial space demand | High, growing cities, expanding middle class |
| Infrastructure & Public-Private Projects | Ports, transport networks, and privatisations | High, Essential projects for improving connectivity |
a. Special Economic Zones & Policy Supports
Pakistan has established Special Economic Zones (SEZs) to attract foreign investment, offering numerous incentives, such as tax breaks and reduced tariffs. A notable example is the Islamabad Model Special Economic Zone, designed to attract $2.5 billion in investments.
These zones offer streamlined processes, dedicated infrastructure, and other incentives to make business operations smoother and more profitable for foreign investors.
Key policy supports include:
- Pakistan Investment Policy 2023: Designed to enhance the business climate by reducing barriers for foreign investors.
- Board of Investment (BOI) and Special Investment Facilitation Council (SIFC): These institutions work closely with foreign investors to ensure smoother processes and faster project approvals.
These policies and SEZs are designed to foster a more investor-friendly environment, making Pakistan an increasingly attractive investment destination.
b. Growing Sectors to Watch
- Technology & Digital Economy:
- Pakistan’s IT outsourcing and fintech sectors are rapidly growing.
- The country is emerging as a hub for global IT companies due to its skilled workforce and competitive costs.
- Fintech innovations are gaining traction, with growing demand for digital payment solutions and financial inclusion.
- Green Energy & Solar Power:
- Pakistan has vast solar power potential, with high solar radiation levels.
- The government is offering incentives for solar power projects as part of its renewable energy goals.
- This sector presents a promising opportunity for foreign investors, given the global push for green energy.
- Manufacturing & Exports:
- Garments and electronics manufacturing are expanding due to both domestic and international demand.
- Pakistan’s competitive labour costs and improving industrial infrastructure create significant growth opportunities in these sectors.
- Agriculture & Food Processing:
- Agriculture remains a critical part of Pakistan’s economy, and food processing is a growing investment area.
- The country’s large domestic market, combined with modernisation efforts in agriculture, offers potential for food exports and agribusiness investments.
c. Real Estate & Urban Growth
As Pakistan undergoes rapid urbanisation, the demand for housing and commercial space is on the rise. Key points include:
- Growing Cities: Major cities like Lahore, Karachi, and Islamabad are seeing increased demand for residential and commercial properties.
- Expanding Middle Class: An increasing middle class is driving demand for better housing and commercial spaces.
These trends create lucrative investment opportunities in real estate development and urban infrastructure.
d. Infrastructure & Public-Private Projects
Pakistan’s infrastructure is set for major growth, with ongoing privatisations and large-scale public-private partnership (PPP) projects. Investment opportunities include:
- Ports: Expanding Pakistan’s trade capacity.
- Transport Networks: Upgrades in roads, railways, and public transport systems.
- Privatisation Efforts: The government is privatising key sectors, creating opportunities for foreign investments in utilities, telecom, and energy.
These infrastructure developments offer long-term investment potential and are key to improving the country’s economic connectivity.
Challenges & What Needs Improvement
While Pakistan offers significant opportunities for foreign direct investment, several challenges still need to be addressed to unlock its full potential. Here are the key concerns for investors:
- Regulatory Red Tape and Bureaucratic Delays
- Complex and slow regulatory procedures
- Lengthy approval processes for permits and business setups
- Bureaucratic hurdles that can discourage foreign investors looking for efficiency
- Security and Political Risk Perceptions
- Internal political instability and regional tensions contribute to security concerns
- Frequent changes in government and policies create uncertainty
- Lack of long-term stability in laws and regulations
- Currency Volatility and Macroeconomic Instability
- Frequent fluctuations in the exchange rate cause financial losses for investors
- Inflationary pressures and unpredictable fiscal policies
- Economic instability can undermine investor confidence
- Dependency on IMF/Loans
- Heavy reliance on the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and foreign loans
- Fiscal constraints imposed by loan agreements reduce government spending on development projects
- Policy adjustments under IMF programs may limit incentives for foreign investors
- Infrastructure Gaps
- Gaps in transport, energy, and communications infrastructure
- Poor infrastructure increases operational costs and affects business efficiency
- Infrastructure deficiencies can deter large-scale investments
Government Initiatives & Reforms
The Pakistani government has introduced several key initiatives and reforms aimed at boosting Foreign Direct Investment. These efforts are designed to attract foreign capital, streamline investment processes, and improve the overall investment climate.
Adoption of Newer Investment Policies to Attract Foreign Investment
- Pakistan Investment Policy 2023: Aimed at providing better incentives for foreign investors, including tax exemptions, ease of doing business, and improved legal protections.
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs): Establishment of SEZs across Pakistan to offer investors benefits such as tax holidays, reduced tariffs, and fast-tracked infrastructure development.
- Greenfield Investments: Promotion of new, foreign-owned businesses to invest in Pakistan’s sectors like manufacturing, technology, and renewable energy.
- Reforms in Taxation: Simplification of tax systems to make investing in Pakistan more transparent and predictable for foreign companies.
- Attractive Terms for Foreign Investors: The government is also offering guarantees for the repatriation of profits and capital.
Institutional Frameworks (SIFC) to Fast-Track Foreign Projects
- Special Investment Facilitation Council (SIFC): A dedicated government body formed to expedite the process of foreign investment. SIFC is responsible for resolving bureaucratic hurdles, offering one-window operations for investors, and overseeing high-priority projects.
- Streamlined Approvals: SIFC provides a fast-tracked approval process for foreign projects, including necessary permits and licenses, making it easier for foreign companies to set up operations in Pakistan.
- Policy Coordination: SIFC coordinates with multiple government departments to ensure a unified approach toward investment attraction and facilitates dispute resolution.
Privatisation Efforts (E.g., Major Sales Like PIA)
- Privatisation of State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): The government has been gradually privatising major state-owned enterprises (SOEs) like Pakistan International Airlines (PIA), Pakistan Steel Mills, and others. These privatisations are designed to attract foreign investors and bring in capital and expertise to improve efficiency.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Encouraging foreign investment through PPPs in sectors such as infrastructure, energy, and transport, creating opportunities for foreign companies to manage and invest in key sectors.
- Boost to FDI: These privatisation efforts indirectly stimulate Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan by opening up state-owned industries to the global market, creating space for foreign expertise and investment in sectors that were previously under government control.
Conclusion | Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan
In conclusion, Pakistan is actively enhancing its investment climate through policy reforms, institutional frameworks like SIFC, and privatisation efforts. These initiatives aim to attract foreign direct investment, offering significant opportunities in sectors such as energy, technology, and infrastructure, positioning Pakistan as an appealing destination for global investors in 2025.
This was all about Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan. For more information on relevant topics such as cryptocurrency vs real estate, visit Chakor Ventures.

